Face anti-spoofing is detecting and preventing attacks on facial security system using photos, videos, or masks.

Domain Generalization is required to enhance robustness against variations, such as different devices and environments.

Model Reliability is crucial because unstable predictions can lead to unauthorized access or denial of legitimate users, undermining overall security system trustworthiness.

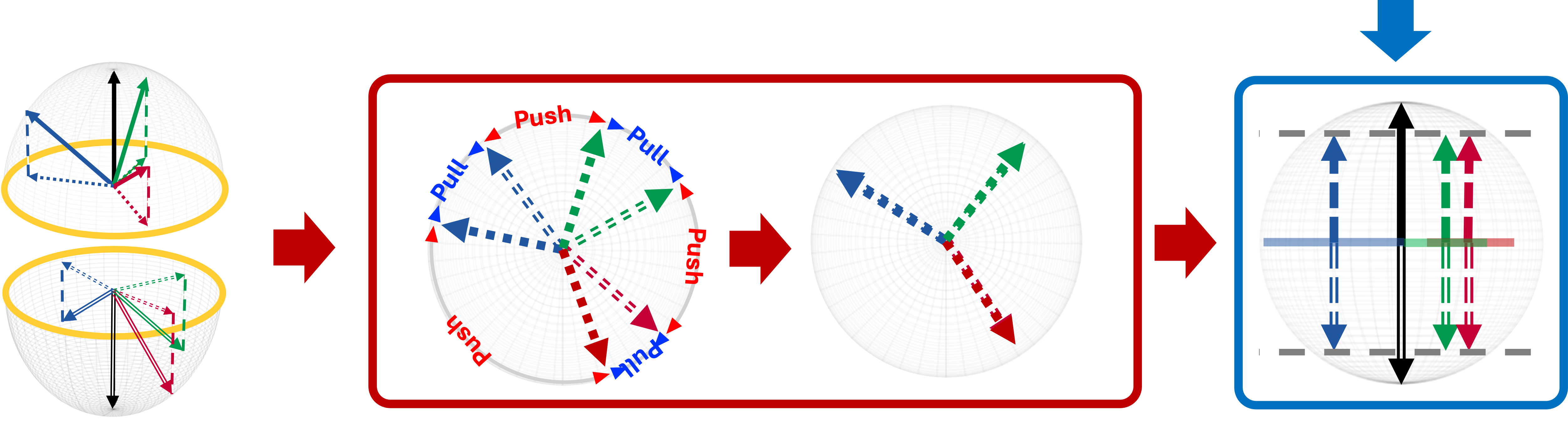
Domain-invariant : consistent for a task (e.g. class) regardless of domains Domain-specific : consistent for a domain (e.g. environment) regardless of the task

Prior work: Aligns only each classifier’s weights for consistent spoof → live direction across domains.
Problem: Output scores remain inconsistent (bias terms misalignment) ⇒ degraded generality
Cause: Classifier bias terms are shaped by the degree of alignment between invariant and specific features, acting as spurious correlations
Challenge: Weights and biases can be aligned across domains, but performance on unknown targets is hard to guarantee
Representation Learning: learns both spaces, aligns bias & weight
Orthogonal Decomposition: invariant & specific features no longer aligned with each other

Image-Text Similarity Loss via Group-wise Scaling Risk Minimization
Bias term alignment in domain-invariant space ⇒ output score consistency regardless of domains.

Feature Orthogonal Decomposition Loss
Weight alignment in domain-specific space ⇒ consistent spoof→live direction across domains.
Benchmark

Reliability with ECE

2D Visualization

@InProceedings{Jung_2025_ICCV,
author = {Jung, Seungjin and Lee, Kanghee and Jeong, Yonghyun and Noh, Haeun and Lee, Jungmin and Choi, Jongwon},
title = {Group-wise Scaling and Orthogonal Decomposition for Domain-Invariant Feature Extraction in Face Anti-Spoofing},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
month = {October},
year = {2025},
pages = {13372-13381}
}